Introduction to Websockets
14.6 min read | January 18, 2024 Click to Share
Click to Share👋 Welcome to Introduction to Web Sockets
Once upon a time when internet was at it's development phase, there lived a man named Abhaya who had a girlfriend ( imaginary ofcourse 🥲), he wanted to talk to his girlfriend. Being a developer, Abhaya created an app using http method. He created a database where he would store all the chats and he would then fetch all the data and then render on a screen. Such was his invention, which in future came to be known as chatting App.
But as always, his girlfriend shouted at him : "What Rubbish website have you built! I have to Refresh the website everytime to check if you have sent any new message to me or not..." These words made Abhaya question himself "Is this method correct ?"
This lead Abhaya to go back to the fundamentals of the Request and Response and the channel by which this communication is made. He then decided to make a new type of connection which will ensure the connection to be open till he and his girlfriend chat and not to close this till they had shared all their stories. This type of connection later came to be known as Web Socket Connections.
Hello Everyone!, hope you liked the story 😂
My name is Abhaya Shankar and I will be your instructor for this short crash course where I will teach you all you need to know before you start working with websockets.
📖 What You will be learning ?
- What are widely used network protocols and how do they work ?
- What is the difference between HTTP Polling, HTTP Streaming, SSE, and Web Sockets ?
- Working of Web Sockets...
- How exactly do websockets work?
- How to create websockets.
- Real-time Examples where Web sockets are used.
- Scenarios where you should be using websockets and where not to.
🤏 Prerequisites
- If you have worked with javascript and React, then you will be good to go.
- Basic knowledge of Nodejs. (Beginners also can follow this)
- You need to have Node installed.
- Interest to learn something new 💡.
- And a cup of coffee. ☕
🛜 Network Protocols and their Working
Before we start our topic on websockets, it's essential to know about the different protocols and why the need for web sockets came in the first place.
There are fair share of protocols used on day-to-day basis but we remain to seem unfamiliarised with them. Let's quickly talk about them and we will then jump back to our discussion here. We are going to talk about all the protocols but our discussion will be limited to the protocols which concerns to this topic. To name a few they are HTTP/HTTPS, TCP, IP and UDP.
- HTTP/HTTPS : Which stands for HyperText Transfer Protocol ( HTTP ) is an Application layer protocol used for transmitting hypertexts docs such as HTML. It is the foundation of data communication on the World Wide Web and is essential for web development. Both HTTP and HTTPS are used for transferring data over the web.
The key difference between HTTP and HTTPS is Security. HTTPS stands for HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure. It uses a secure, encrypted connection, typically using SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) or its successor, TLS (Transport Layer Security). This encryption ensures that the data exchanged between the client and server is encrypted, providing confidentiality and integrity.
- TCP/IP : Which stands for Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol specifies how devices exchange data over the internet. They are the fundamental suite of protocols for communication on the internet. TCP ensures reliable, ordered, and error-checked delivery of data.
The TCP defines how application create communication channels and also manages how the data can be broken down into different packets/packages to be then transmitted over the internet and then re-assemble at the destination.
IP defines how to address and route each packet/packages to ensures they are received at the destination.
They are designed for network reliability and auto recovery from failures. If suppose a packet which has to be received at the destination, for some reason didn't arrive at the destination, then the TCP/IP will ensure to look for the lost packet and recover it over the internet.
In Short TCP is designed to ensure reliable and ordered delivery of data. If a packet is lost in transit, TCP employs retransmission mechanisms, flow control, and congestion control to recover the lost data. These mechanisms contribute to the robustness and reliability of TCP/IP-based communication over networks, making it suitable for applications that require accurate and complete data delivery.
- UDP : Stands for User Datagram Protocol. Its working is quite similar to TCP/IP. Here also the data is broken down into packets ( referred to as datagrams ) in the case of UDP protocols but UDP is connectionless, meaning it does not establish a connection before sending data. Each datagram is independent of others, making it faster but less reliable than connection-oriented protocols like TCP. It doesn't have much error checking as compared to TCP. Moreover, in transit, if a datagram is lost, it is not traceable, meaning it cannot be recovered.
In short, UDP is preferred for scenarios where speed and low latency are more critical than ensuring every piece of data is delivered. Its simplicity and reduced overhead make it suitable for real-time applications and situations where occasional packet loss can be tolerated.
Hope, all that made sense to you. Now once we are familiar with these terms. Let's move back to our discussion about web sockets.
In the modern era where internet is used more extensively than anything else, you might have used Whatsapp, Facebook and Instagram. Real-time messaging is one of the key features which was why there messaging social platforms are widely used.
I believe now you know about or atleast heard of HTTP/HTTPS protocol. The working of which is simple where a client sends a request to the server and the request is then processed and if everything is good, server will then send the 200 OK response. If any error or issue with the request, it will send back a 403/404/500 response error depending upon the type of error.
If all these seems gibberish to you, make sure you atleast have a basic knowledge of this. You can refer this Link.
Let's now understand how this would actually work like with a real-scenario based example. Let's say I went to a restaurant to eat ramen 🍜.
I would then ask the waiter for a menu to check which ramen they sell and upon then order.
-
I ( client ) will then order the desired ramen and then the waiter ( connection ) will take up that order to the kitchen ( server ).
-
The chef in the kitchen will then check if they know how to prepare the order ( processing the request ) and then prepare my ramen ( response ).
-
The waiter ( connection ) will then come back to me ( client ) with the finished Ramen ( Response ).
-
If the chefs in the Kitchen don't know how to prepare the ramen then the waiter will come back with apologies ( Error 500 or 404 ) that they couldn't process the order.
Such is the working of the HTTP connections. Now if I wanted to add eggs to the ramen, I would have to call the waiter and let him pass on the message to the chef, and for every request, I would have to call the waiter again and again.
So here's the issue : The kitchen can’t send a waiter to you; it can only give the waiter a dish, or bad news, when you send the waiter over. So, for the client to get updates, the only possible way is to send request to the server.
Such was the issue which Abhaya from the story was facing while he was chatting with his girlfriend. Abhaya was sending message to the server as some request with the payload, server received the message and stored in the database. But his girlfriend had no idea whether Abhaya had sent any message or not. Only way she can get the latest message is by again sending a request to the server to get back the latest response, only then can server send back the new messages.
What if we could have a way to communicate with the chef in the kitchen directly ? Interesting right then no need of contacting the waiter again and again yeah ?
Let's take a food truck instead of a restaurant then what would happen. I would directly talk to the chef of the food truck and would tell the chef that I want to eat ramen, if he knows he would directly tell me if he knows or not. I wouldn't wait for the response to come back and if yes, he knows how to prepare later if I want to add eggs I would directly tell him that I want eggs, please add them too. This type of conversation is more profound and better. Don't you think so ?
Well, you know we are getting to web sockets right. 😂
But before going to that topic, let's discuss what other work around can be for these scenarios if not web sockets or why the need for web sockets arise.
🌐 HTTP Polling, HTTP Streaming and SSE
- HTTP Polling : One dead simple approach to work around this issue was polling. Polling is basically categorised into 2 parts namely SHORT POLLING and LONG POLLING.
-
Short Polling is very simple, just keep spamming server after every fixed amount of time, let's say 1000ms to get back any new messages. In this client keeps calling the server for latest data is any and is acheived using setTimeout and setInterval. Downfall of this is that it consumes server resources with a barrage of requests, and most requests will return empty if the data isn’t frequently updated.
-
Overcoming this issue came Long Polling. In this method, the server also receives a request, but will respond back till it gets any new data from the server. Till then it will be in pending state and won't complete till the request is resolved termed as hanging. Long polling is more efficient than pinging the server repeatedly since it saves the hassle of parsing request headers, querying for new data, and sending often-empty responses. However, the server must now keep track of multiple requests and their order. Also, requests can time out, ensuring low latency, and new requests need to be issued periodically.
- HTTP Streaming :This mechanism saved the pain of network latency because the initial request is kept open indefinitely. The request is never terminated, even after the server pushes the data. The first three lifecycle methods of HTTP streaming are the same in HTTP long polling.
- When the response is sent back to the client, however, the request is never terminated; the server keeps the connection open and sends new updates whenever there’s a change.
- SSE : SSE stands for Server Sent Events. Another technique for sending messages which leverages the Javascript EventSource interface. SSE is a standardized form of HTTP Streaming concept. EventSource opens a persistent, one-directional connection with the server over HTTP using a special text/event-stream header and listens for messages.
- This is almost what we’re looking for. Now we can now receive updates from the server! Because they’re one-directional, Server-Sent Events (SSE) are great for apps where you don’t need to send the server any data. For example, the Facebook News Feed: whenever new posts come in, the server pushes them to the timeline.
- Web Sockets : Web Sockets are the technology that is built on full-duplex connection i.e. it allows client and server to communicate with each other in real time over TCP connection. The Keyword here is two-way communication. Web Sockets allow client and server to trigger communication with one another gaining upper hand on Polling, Streaming and SSE Events.
Moreover, the server can keep track of each client and push messages to a subset of clients. With this technology, now Abhaya and his girlfriend can chat without any disturbances.
Key Points About Web Sockets
- Web Sockets are Bi-directional in nature
- Web Sockets uses TCP connection
- Connection developed using web sockets will last as long as client and server don't close the connection.
- Web Sockets uses HTTP to initiate the connection.
🪄 Wooaahh! You made it this far..
Give yourself a pat on the back. You did great. If you are this far, only a few more to go till you get a complete gist of the technology we are trying to learn. You are awesome! Take a sip of coffee or tea and let's continue... 🤩🤩
🪄 Working of Web Sockets
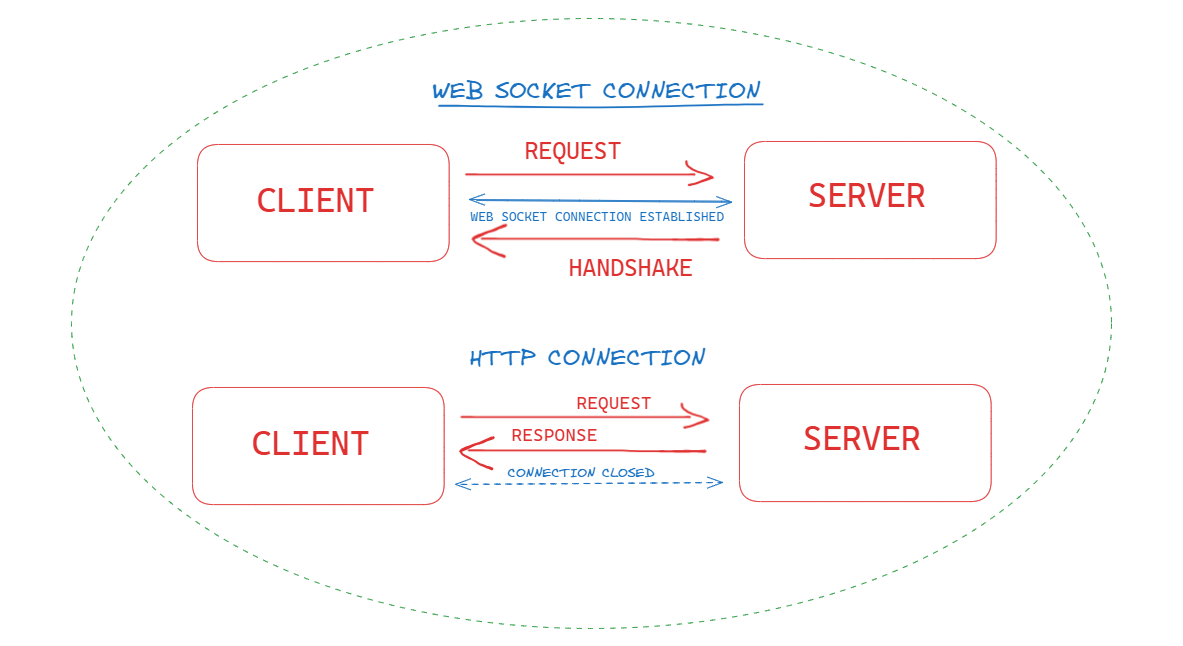
Web socket connections are established by an upgraded version of HTTP Request/Response pair. A client which wants to support a web socket connection will send a HTTP Request with the following headers :
-
Connection: Upgrade : The
Connectionheader typically manages the persistence of the network connection beyond the current transaction. A common value for this header iskeep-aliveensuring that the connection remains open to accommodate subsequent requests to the same server. -
Upgrade: WebSocket : The
Upgradeheader is used by clients to ask the server to switch to one of the listed protocols, in descending preference order. We specifywebsockethere to signal that the client wants to establish a WebSocket connection. -
Sec-WebSocket-Key: Secret_WS_Key : The
Sec-WebSocket-Keyis a one-time random value (a nonce) generated by the client. The value is a randomly selected 16-byte value that has been base64-encoded.
Altogether, the connection established using GET Request, looks something like this :
GET ws://example.com:8181/ HTTP/1.1
Host: localhost:8181
Connection: Upgrade
Pragma: no-cache
Cache-Control: no-cache
Upgrade: websocket
Sec-WebSocket-Version: 13
Sec-WebSocket-Key: a7xkcO328466gldTuKaSUa==
Once a client sends the initial request to open a WebSocket connection, it waits for the server’s reply. The reply must have an HTTP 101 Switching Protocols response code. The HTTP 101 Switching Protocols response indicates that the server is switching to the protocol that the client requested in its Upgrade request header.
For establishing a web socket connection, first the client sends a request to the server. Upon receiving the request, server then returns back a response and till this response is valid, the open connection persists till any of the client disconnects. This process is called Handshake. With every new request, a new TCP connection is generated and the previous connection is terminated.
The Handshake from the server looks something like this :
HTTP/1.1 101 Switching Protocols
Upgrade: websocket
Connection: Upgrade
Sec-WebSocket-Accept: s3pPLMBiTxaQ9kYGzzhZRbK+xOo=
Sec-WebSocket-Protocol: chat
Web Sockets are such connections where the client and the server communicates with an open channel. If the server would want to transmit/send any data to the client it would do so directly.
Now if the client or server anyone closes the channel, the connection is closed.
Ex. If you have had your fair share of food and you would want to go now. You ( client ) will close this channel and the connection will be closed If the Shop owner wants to close the shop, then he will terminate the channel and the connection will be closed.
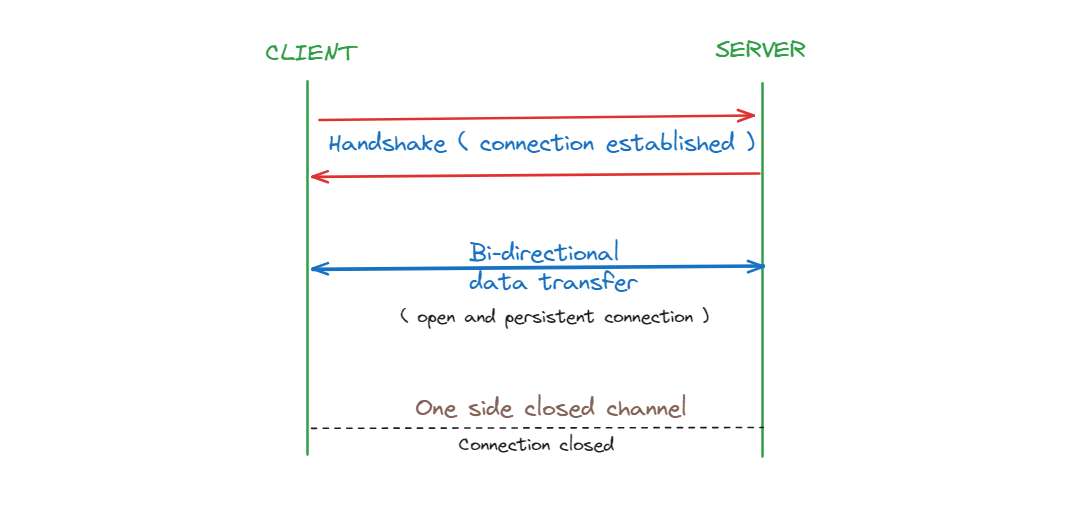
Websockets are very powerful when it comes to bi-directional communication and read time updation with minimum overhead. Fragmentation makes it even more powerful and light weight. You should understand web socket protocol and what are the underline priniciples of it and how it works.
Hope this Blog helped you ... 😊
🤩 Congratulations! You did it 🔥🔥
Great! You have successfully completed this comprehensive blog on web sockets.
You deserve a toast 🥂. Now you can proceed with some new ideas to create a chat App using web sockets. If you have been following up and have created something, make sure to showcase your project connect with me on LinkedIn.
Here's the LINK to the new blog for how to create and start working with web sockets.
